Chiba University IAAR
Creation of ultrasonic pathology and establishment of non-invasive multiscale quantitative diagnostic method
Chiba University IAAR
Creation of ultrasonic pathology and establishment of non-invasive multiscale quantitative diagnostic method
In order to understand the extent of changes in internal tissues due to cancer and other diseases, as well as the progression of various diseases, blood tests, imaging diagnosis, and pathological tests are carried out, in which the target tissue inside the body is extracted with a needle and observed under a microscope. Each of these tests has its advantages and disadvantages, but because they place a considerable burden on the patient's mind and body, there is a need to establish simple, highly accurate diagnostic methods.
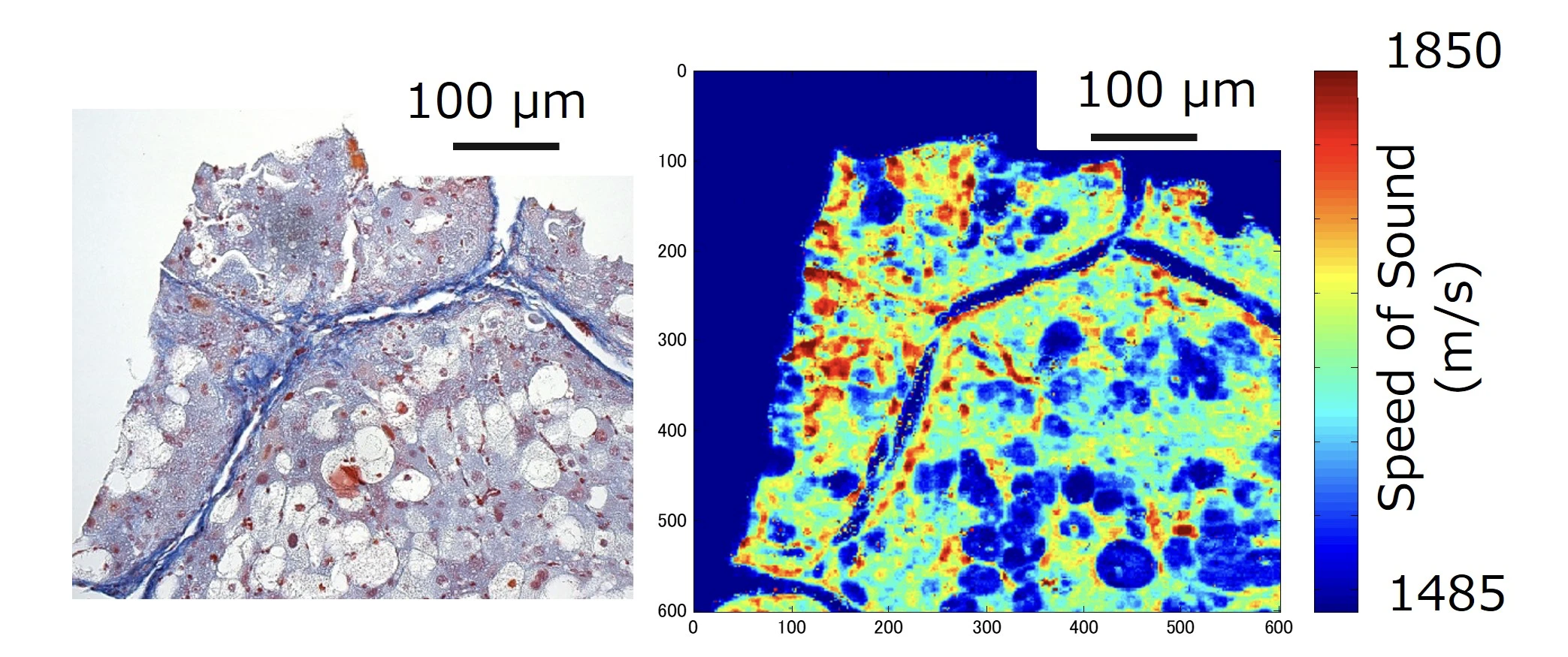
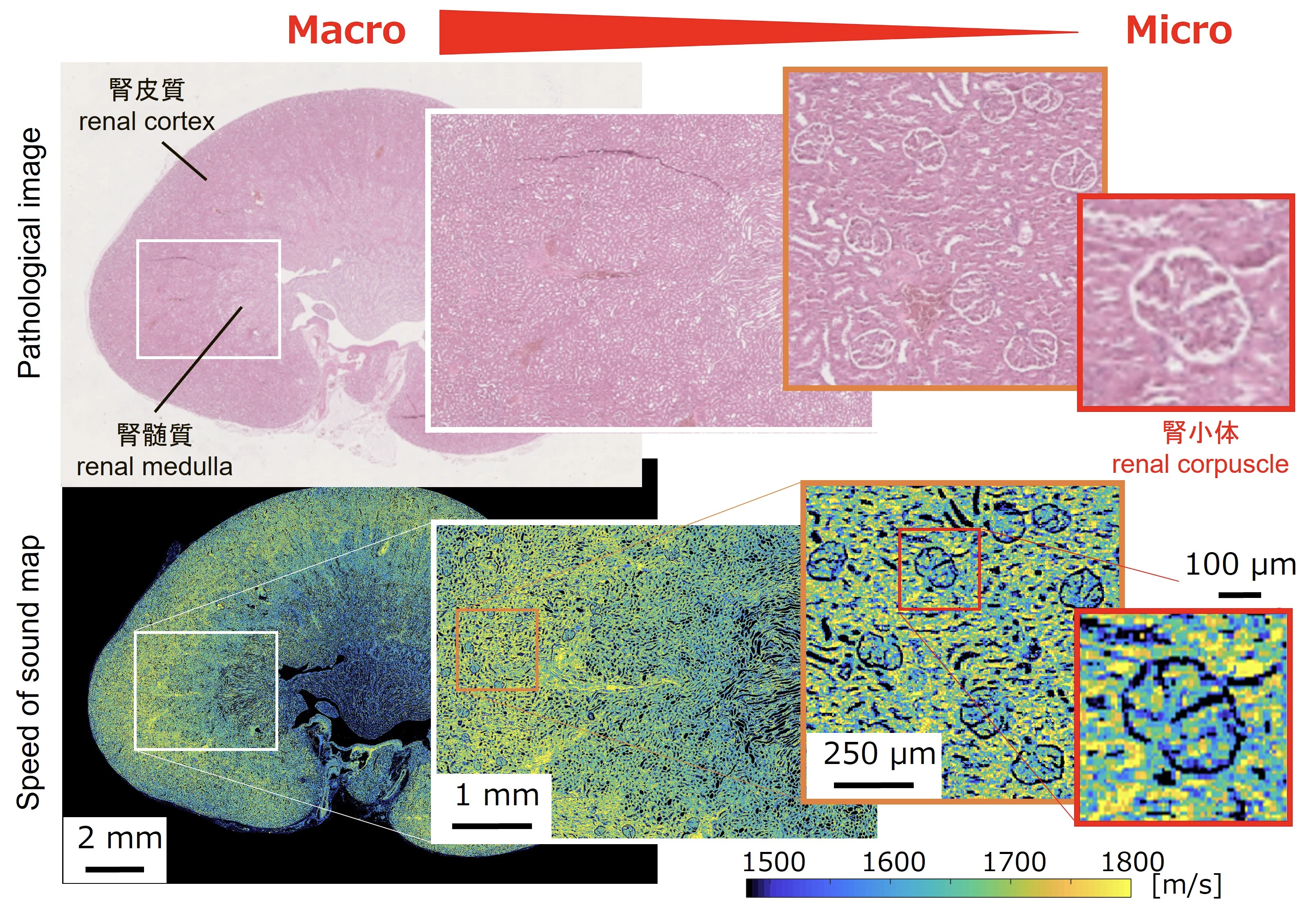
In this study, we will make the most of the ability of ultrasound to evaluate the hardness and shape of materials in real time, and we will evaluate the “properties of living cells” and “relationship between structure, composition, and properties/state (characteristics)” of biological tissues in the body microscopically (microscopic) and macroscopically (macroscopic), and we will realize a quantitative diagnostic method “non-invasive pathology” that can directly link the physical properties of biological tissues that cannot be understood by existing tests and the we have achieved a quantitative diagnostic method that can directly link the relationship between the physical characteristics of biological tissue and its properties from a medical perspective on a multi-scale basis. In other words, it means that it is possible to obtain the same results as evaluating the state of cells removed with a needle, and to predict things like cancer risk, etc., non-invasively and without blood sampling, simply by observing the tissue to be diagnosed from outside the body using ultrasound.
This “non-cutting pathology testing” technology is not only useful for diagnosis, but also for confirming the condition of the target tissue before and after surgery, and it can also be used to improve safety and accuracy during surgery by evaluating tissue properties in real time. In addition, by reducing the frequency of testing using this technology, it can reduce the burden on patients as well as doctors and technicians working in clinical settings, and it can also reduce medical costs.
The comprehensive biological properties database that will be created through this research, which will compile the properties of biological tissues in various states, as well as their acoustic, mechanical and biochemical properties, will create a new academic discipline called “ultrasound pathology”. It will also serve as a biomarker (an indicator of biological and pathological changes and conditions, as well as the effects of treatment) that can be applied to various medical imaging diagnostics such as CT and MRI, and will greatly contribute to the “standardization of imaging diagnostics” that is not dependent on the conditions of the equipment or settings.
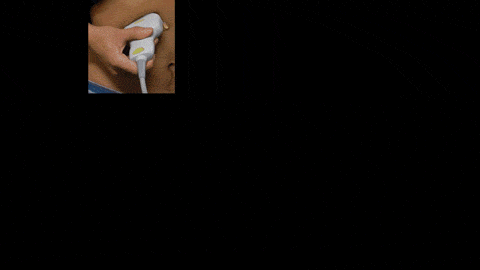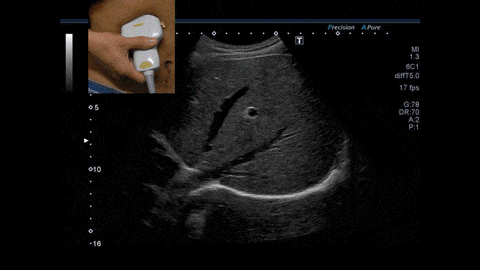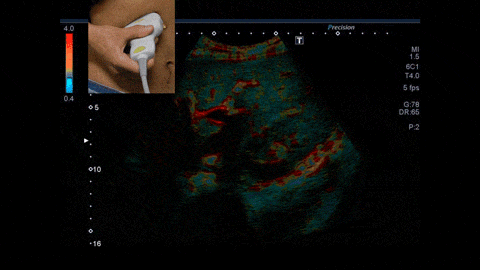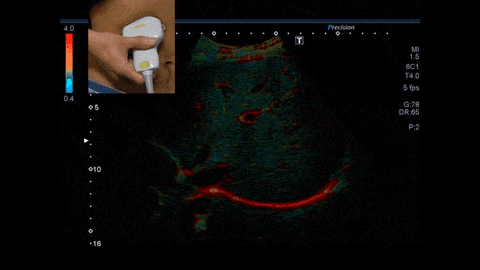
Chiba University formulated the "Chiba University Aspirations" on July 3, 2021.The university lays out the following four research goals to promote the world-leading research and establish a hub for Global Brain Circulation:
1. Appreciate academic diversity to encourage creative research
2. Promote world-class academic research to pioneer new interdisciplinary research fields
3. Accelerate innovative research to create new academic value
4. Establish a research-faculty organization, "International Strategic Research Institute